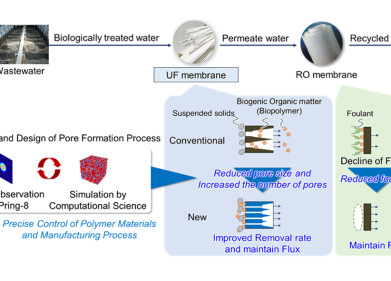
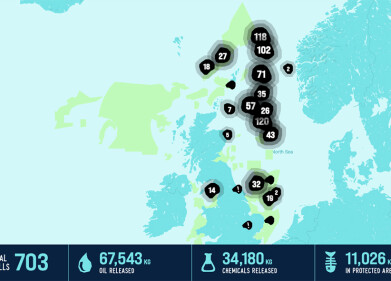
Water/Wastewater
MicroCat-ANL reduces H2S in municipal sewer lines
Dec 12 2012
In a pilot application in the south of England, MicroCat-ANL was tested to control H2S formation in a pumping station at the head works of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. The sewage arrived at the station through two large sewer lines with a length of subsequently 2 and 2,5 miles. The H2S was continuously monitored at the receiving pumping station. From the pumping station the sewage was pumped into the head works building of the treatment plant. In order to preserve the concrete and metal and too maintain proper health and safety conditions for the workers a limit of 10 ppm H2S was adopted by the wastewater treatment company.
Two upstream pumping stations where selected as dosing points. The first upstream pumping station operates at a flow rate of 80 m3/day and the hydraulic residence time of the sewage from this pumping station to the receiving station is approximately 11 hours. The other pumping station operates at 1800 m3/day and the hydraulic residence time of the sewage is approximately 9 hours. Because of the long hydraulic residence times H2S formation inside the sewer lines was a major problem.
QM Environmental Services and it's UK distributor Cobra Hydro UK Ltd. designed a dosing scheme for MicroCat-ANL which would stay within the allocated budget from the wastewater treatment company and would keep the H2S formation below the 10 ppm as much as possible. Dosing started on the 16th of April 2012 with a 10 day start up program followed by a daily maintenance dose which continued through the spring and summer of 2012. Dosing was stopped on the 20th of October.
The attached graph image displays the H2S levels in the receiving pumping station just prior to and during the pilot period. MicroCat-ANL was able to reduce H2S levels below 10 ppm for the majority of the time. The spike in H2S levels at the end of May is due to the fact that the dosing was stopped on the 15th of May to see if a lagging effect of the treatment occurred. It took over 2 weeks before the H2S levels started to exceed the 10 ppm barrier, despite warm weather conditions in that period. Soon after dosing restarted again the H2S levels started to decline again. End of July hot weather increased H2S levels to just over the 10 ppm limit, this period lasted up to the end of September.
Overall MicroCat-ANL did a good job reducing H2S especially considering that other pumping stations in the same area experienced much higher H2S levels with spikes up to 80 ppm and higher. Additionally, operators of the municipal wastewater treatment plant reported improved settling, reduced DO requirements and reduced foaming since ANL was used.
For more information contact QM Environmental Services.
Events
Mar 18 2025 Expo Santa Fe, Mexico
Mar 18 2025 Moscow, Russia
Mar 19 2025 Manila, Philippines
Mar 20 2025 Guangzhou, China
Mar 24 2025 National Harbour, MD, USA